The history of the use of feminine pads goes back to the distant past. Menstruation and women's health issues forced women to get creative. The pads were made from various fabrics, animal skin, and papyrus. A few decades ago, our mothers used cotton wool, gauze, and cotton fabric. The life of a modern woman has been simplified by sanitary pads, which appeared 15-20 years ago. Manufacturers took into account all the wishes of women and created products that meet hygiene requirements.
Today there is a wide variety of gaskets on the shelves of pharmacies and stores. Women have the opportunity to choose according to the individual characteristics of the body. The scope of application is by no means limited to use on menstrual days. All types pursue a single goal - to make a woman’s life easier during periods of temporary difficulties, to absorb liquid.
What kind of modern gasket is it?
The purpose of the product is to absorb vaginal discharge. Be it menstrual periods, daily leucorrhoea, urine leakage. Hygienic products for absorbing menstrual flow must meet the following requirements: absorb moisture well, do not release it back, and do not change shape. The woman is already accustomed to this and chooses just such pads for herself. They are made from synthetic materials. Because natural fabrics cannot ensure the fulfillment of a woman’s wishes. But there are hypoallergenic pads, the top layer of which remains natural.
Daily hygiene products are practically no different from the previous ones in composition. The materials used are the same. Thickness, shape, color changes. Panty liners come in white and black, matching the color of your underwear. To prevent odor during menstrual periods and during daily prolonged use, the product is impregnated with scented substances. For better absorption of secretions, a layer of gel is placed inside. The same applies to urological pads.
A modern woman cannot imagine her life without these hygiene products; she uses them constantly or periodically.
Classification of flange gaskets and their selection for various flange connections
In hermetic sealing systems for flange connections, used in equipment for the chemical and a number of other industries, detachable connections are used, the performance of which determines the operating pressure limits and the quality of operation of the equipment as a whole.
If a unit or sealing system fails, the unit ceases to be operational, and the risk of an accident increases, which can lead to human casualties and environmental disasters.
Violation of the tightness leads to a violation of the process technology, a decrease in the quality of the resulting product, a loss of raw materials and an increase in the cost of manufactured products.
The quality and reliability of a flange connection largely depends on the sealing gasket ; moreover, the use of gaskets is necessary.
What determines the choice of gasket?
To achieve the required degree of tightness of the flange connection, the following steps must be correctly carried out:
- choice of gasket type,
- choice of gasket design,
- installing the gasket.
A gasket is a separate compressible connection element, which, being in a compressed state between the flanged parts of pipelines, under the influence of pressure from tightened fasteners, fills the gap between the connected parts.
Types of pads for critical days
Hygiene products for menstruation are divided into daytime and nighttime. Each of these types is divided into subspecies, according to their ability to absorb. They differ in size, and on the packaging manufacturers indicate the number of drops and the designations “light”, “normal”, “maxi”. Pads with a normal ability to absorb secretions are designated “normal” with 3 drops. For increased bleeding, hygiene products with 4.5 drops are intended. Next come the night ones. For moderate bleeding, you should choose “normal” with 3 drops.
Interesting video:
During the day, a woman moves more and can afford to change pads several times a day. There should be a full night's sleep. No one will change a hygiene product every 2 hours unless there is such a need. They should absorb more and prevent secretions from leaking. After all, during sleep, the posture can be very different. Thus, the appearance of the night pads has changed somewhat - they have become longer. Otherwise they are no different from daytime ones. Gaskets can be recognized by the packaging without reading the label, not counting the drops. They depict a night with a starry sky. Based on their composition, disposable sanitary pads can be divided into several types:
- With and without an inner layer of gel . The gel helps retain moisture inside the product and prevents it from leaking out. Allows a thin pad to absorb a large amount of secretions on critical days.
- Flavored, odorless . During critical days, a specific smell appears. Not every woman treats him with patience. For some, it simply irritates and reduces self-confidence, since it seems that the people around them feel it. The top layer of the product is impregnated with a flavored substance. Smells like flowers, perfume, and other pleasant aromas.
- With synthetic, natural top layer . Synthetic pads during menstrual periods can cause an allergic reaction to the skin of the perineum. Sometimes it is so strong that it leads to the formation of thrush, inflammation, and other problems with the health of the reproductive system. The woman is forced to replace them with hypoallergenic ones. There is also plenty to choose from. Hypoallergenic hygiene products are no different in appearance. There is a difference in the fabric used. The top layer is made natural, flavors and gel are removed. All auxiliary components that can cause allergies. Such a gasket causes some inconvenience when used on critical days. The top layer does not absorb secretions well enough. The gasket changes shape and causes discomfort when moving.
- With wings, without them . This part of the hygiene products serves to attach to the panties. It allows the gasket to remain in place at all times. Protects underwear from menstruation from the sides. Some hygiene products for critical days do not have wings. The pad is attached to the underwear with glue. It is located on the bottom layer of the gasket. You can choose any type, the main part does not change.
Pads for critical days are made white. This hygiene product looks sterile and safe for a woman’s health. The color of the discharge is clearly visible. During menstruation, it may change, indicating diseases of the reproductive system.
General technical conditions
Official publication
Moscow Standardiform 2020
Preface
- 1 DEVELOPED by the Association of Manufacturers of Perfumery, Cosmetics, Household Chemicals and Hygiene Products (APPIK BH)
- 2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization 157 “Wood Pulp. Paper, cardboard and products made from them"
- 3 APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated August 11, 2021 No. 484-st
- 4 INSTEAD GOST R 52483—2005
The rules for applying this standard are established in Article 26 of the Federal Law of June 25, 2015 Ns 162-FZ “On Standardization in the Russian Federation”. Information about changes to this standard is published in the annual (as of January 1 of the current year) information index “National Standards”, and the official text of changes and amendments is published in the monthly information index “National Standards”. In case of revision (replacement) or cancellation of this standard, the corresponding notice will be published in the next issue of the monthly information index “National Standards”. Relevant information, notices and texts are also posted in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet (www.gost.ru)
© Standardinform. decor. 2020
This standard cannot be fully or partially reproduced, replicated or distributed as an official publication without permission from the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology
GOST R 52483—2020
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
WOMEN'S HYGIENIC PADS (PACKAGES)
General technical conditions
Hygienic pads for women. General specifications
Date of introduction: 2020—11—01
1 area of use
This standard applies to feminine sanitary pads (bags) (hereinafter referred to as pads) and establishes requirements for their quality. This standard does not apply to pads intended by the manufacturer for medical use for people suffering from diseases of the genitourinary system or other diseases with impaired control of excretory function. The requirements to ensure the safety of pads for women's health are set out in 4.11.4.12, Table 1 (indicators 3.4).
2 Normative references
8 of this standard uses normative references to the following standards:
GOST 15.009 System for developing and launching products into production. Non-food consumer goods
GOST 427 Metal measuring rulers. Specifications
GOST 1770 (IS01042-53. ISO 4788-80) Laboratory glassware. Cylinders, beakers, flasks, test tubes. General technical conditions
GOST 4233 Reagents. Sodium chloride. Specifications
GOST 4568 Potassium chloride. Specifications
GOST 6658 Paper and cardboard products. Packaging, labeling, transportation and storage
GOST 6709 Distilled water. Specifications
GOST 10354 Polyethylene film. Specifications
GOST 10700 Waste paper and cardboard. Specifications
GOST 12026 Laboratory filter paper. Specifications
GOST 12523 Pulp, paper, cardboard. Method for determining the pH value of an aqueous extract
GOST 14192 Marking of cargo
GOST 15150 Machines, instruments and other technical products. Versions for different climatic regions. Categories, operating, storage and transportation conditions regarding the impact of environmental climatic factors
GOST 28498 Liquid glass thermometers. General technical requirements. Test methods
GOST 33781 Consumer packaging made of cardboard, paper and combined materials. General technical conditions
GOST R 55227 Water. Methods for determining formaldehyde content
Official publication
GOST ISO 10993*10 Assessment of the biological effect of medical devices. Part 10. Studies of irritant and sensitizing effects
Note - When using this standard, it is advisable to check the validity of the reference standards in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet or according to the annual information index "National Standards", which was published as of January 1 of the current year, and on issues of the monthly information index “National Standards” for the current year. If an undated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended that the current version of that standard be used, taking into account any changes made to that version. If a dated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended to use the version of that standard with the year of approval (adoption) indicated above. If, after the approval of this standard, a change is made to the referenced standard to which a dated reference is made that affects the provision referred to, it is recommended that that provision be applied without regard to that change. If the reference standard is canceled without replacement, then the provision. in which a link to it is given, it is recommended to apply it in the part that does not affect this link.
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms with corresponding definitions are used in this standard:
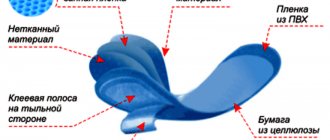
- 3.1 feminine sanitary pads (bags): Multilayer absorbent disposable products designed to absorb and retain external secretions in women during the menstrual period (for critical days) and the intermenstrual period (daily, for every day, etc.) and used in as personal hygiene products.
- 3.2 top cover layer: The layer that is in direct contact with the skin and allows secretions to pass into the pad.
- 3.3 distribution layer: The layer that is located behind the top cover layer and promotes uniform distribution of liquid inside the gasket.
- 3.4 absorbent layer: The inner main absorbent layer of a pad that absorbs and retains the absorbed liquid.
- 3.5 protective layer: The layer that is located directly behind the absorbent layer and prevents the penetration of secretions onto the laundry.
- 3.6 lower covering layer: The layer that is located behind the protective layer and is furthest away from the body.
- 3.7 fixing layer: An adhesive layer that is applied to the bottom cover layer to fix the pad to the laundry.
- 3.8 release layer: The layer that covers the fixing layer.
- 3.9 wings: Elements of the technical design of the pad, which are located on its sides, are wrapped over the edge of the linen and fixed on it to more firmly secure the pad to the linen.
- 3.10 special ingredient: A substance or material that is intended to give gaskets, in addition to the basic functional properties, a number of additional properties (odor absorbent, etc.).
- 3.11 superabsorbent: A chemical substance in the form of granules designed to increase the absorbency of a pad.
- 3.12 individual packaging: Packaging for one individual pad.
4 Technical requirements
- 4.1 Gaskets are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to technical documentation (technological regulations, technical description, etc.) for a specific gasket and/or group of gaskets. If necessary, a standard sample in accordance with GOST 15.009 is approved for gaskets.
4J Gasket design requirements
- 4.2.1 The main components of the construction of pads are (starting with the layer in contact with the skin): the top cover layer, the distribution layer, the absorbent layer, the protective layer, the outer cover layer, the fixing layer and the anti-adhesive layer, which are 2
plexes ensure the absorption of the released liquid and its retention inside the pad, as well as fixing the pad on the underwear.
It is allowed to produce gaskets without a distribution layer and without a lower covering layer. In the latter case, the functions of the lower covering layer are performed by the protective layer.
In individually packaged gaskets, the adhesive layer may be the individual package itself.
Gaskets may have additional layers in addition to those specified in this paragraph that perform certain functions.
- 4.3 Technical design of gaskets
- 4.3.1 Gaskets can be rectangular. ELLIPSOIDAL or other shape.
- 4.3.2 Gaskets are made with or without wings, smooth or embossed, white or colored, scented or unflavored. with or without superabsorbent, in individual packaging or without it. Other types of technical design of gaskets are allowed.
- 4.4 Decorative design of gaskets
- 4.4.1 Gaskets are manufactured without finishing or with finishing using a pattern applied in various ways (printing, embossing, etc.), or other methods.
- 4.5 The design of gaskets, linear dimensions, technical and decorative design of gaskets are indicated in the manufacturer’s technical documentation for specific gaskets or a group of gaskets.
- 4.6 The following materials are used for the manufacture of gaskets:
- - for the upper and lower covering layers: microporous polymer film, non-woven material or other materials with quality indicators that ensure the manufacture of gaskets in accordance with the requirements of this standard:
- - distribution layer: non-woven material or paper intended for household and sanitary products, a mass of paper made from cellulose and wood pulp. The use of paper for household and sanitary products made from waste paper and cardboard according to POST 10700 is not allowed:
- — absorbent layer: fluff pulp or other materials of synthetic or natural origin. To increase absorbency, the absorbent layer may contain superabsorbents;
- — protective layer: polymer film or other materials that prevent the penetration of secretions onto the laundry;
- — fixing layer: hot melt glue or other material with adhesive properties that ensures the pad is fixed to the underwear;
- - anti-adhesive layer: paper with an anti-adhesive coating, for example silicone paper or other material with anti-adhesive properties;
- — individual packaging: polymer film, including painted film, or other material at the discretion of the manufacturer;
- — special ingredients: mineral sorbents, flavored additives and other substances.
- 4.7 The fixing layer must be applied to the bottom covering layer, and in its absence - to the protective layer and ensure strong attachment of the pad to the laundry.
- 4.8 The anti-adhesive layer must completely cover the fixing layer.
- 4.9 Layers of gaskets are fastened using heat treatment, or hot melt adhesive, or another method that ensures the strength of gluing of the layers (seam) of the gasket. The seams must be continuous.
- 4.10 Raw materials and materials for the manufacture of gaskets are indicated in the technical documentation - specific gaskets or a group of gaskets.
- 4.11 Raw materials for the manufacture of gaskets must comply with the requirements of regulatory documents in force in the territory of the state that has adopted the standard.
- 4.12 Quality indicators (indicators 1. 2) and safety (indicators 3. 4) of gaskets must meet the requirements specified in table 1.
Table 1
| Indicator name | Indicator value | Test method | |
| Daily pre-laying | Pads for use during the menstrual period | ||
| 1 Complete alago absorption. no less | 1 | 10 | According to 6.4 |
| 2 Absorption time, s. no more | 10 | Software 6.5 | |
| 3 Change in pH of aqueous extract | No more than +/- 1 unit. | According to GOST 12523 and 6.6 | |
4 Hygienic indicators:
| 0.1 0.1 0J 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.1 0,5 0.5 0.02 0.25 0.02 0,01 | According to 6.8 | |
| 4.2 Toxicity index of aqueous extract*. % | From 70 to 120 incl. | ||
| 4 3 Sensitizing ability index (/,), point | 0 | ||
| * Research is carried out on aqueous model extracts from the specified products. Note - Indicators 4.1.9—4.1.12 are determined only for pads that contain superabsorbent. |
- 4.13 Appearance requirements
- 4.13.1 The following are not allowed in gaskets: folds, mechanical damage, stains of various origins. foreign inclusions not provided for in the technical documentation, visible to the naked eye.
Inclusions (traces) of special ingredients are allowed that do not impair absorbency.
- 4.13.2 The printed image on the gaskets must be clear, without distortion or gaps. Traces of plucking fibers from the surface of the gasket and marking off the paint are not allowed.
- 4.13.3 The colorful background of colored gaskets must be uniform, without gaps not provided for in the technical documentation. Dye set-off is not allowed.
- 4.13.4 The embossing relief must be smooth, clear, without gaps, visible to the naked eye.
4.14 Marking
4.14.1 Marking should be applied directly to the packaging or to a label (label) attached to the packaging. The marking is applied in any way (printing, embossing, stamping) that ensures its clarity, clarity and readability. When using the printed method of marking, ink set-off is not allowed.
- 4.14.2 Marking of gaskets must contain the following information:
- • product name;
brand name (if necessary) and product designation assigned by the manufacturer (can be indicated in Latin letters);
- — name of the manufacturer (manufacturer), its location (address of the legal entity) (can be indicated in Latin letters):
- - for imported goods - name of the country of origin of the goods;
- • name, address or telephone number of the organization authorized by the manufacturer to accept claims from the consumer (if the manufacturer does not accept claims in the territory of the state that has adopted the standard). The telephone number intended for receiving complaints can be presented in the “Hotline” format;
- — expiration date in the format: date of manufacture (month of year) and expiration date (month of year) or the inscription “best before” (month of year) or “use by” (month of year). The phrase “date of manufacture” in the marking of gaskets can be replaced by the phrase “date of manufacture” or words of similar meaning. The words “best before”, “use before” in the labeling of gaskets can be replaced by the words “use before” or words similar in meaning;
- — batch number or special code assigned by the manufacturer, allowing identification of a batch of products (the code can be the date of manufacture);
- — designation of this standard (for products manufactured in accordance with this standard);
- — number of gaskets in the package;
- — instructions for disposal in the form of inscriptions or graphic images (for example: “Do not throw into the sewer”);
- — designation of consumer characteristics of gaskets in accordance with the manufacturer’s classification. in the form of inscriptions and (or) graphic images (shown in Appendix A).
If it is impossible to place the necessary information on the product or packaging (small sizes and shapes of the product), it must be presented on labels, labels, insert cards, etc., attached or attached to the product.
- 4.14.3 Marking of packages (transport packaging) - in accordance with GOST 14192 with the application of the handling sign “Keep away from moisture”.
- 4.15 Packaging
4.15.1 Gaskets in individual packaging or without it, several pieces, are packed in plastic film bags, or in packs, or in boxes in accordance with GOST 33781. or in other packaging that ensures the safety of the gaskets during transportation and storage.
- 4.15.2 Gaskets of the same name, type, class are packed in one bag, pack or box. designs, linear dimensions, thickness, technical and decorative designs, made from the same materials, with the same quality indicators.
4.15.2.1 It is permissible, by agreement with the consumer, to pack individually packaged gaskets of different linear dimensions, types, technical and decorative designs into one bag, pack or box if there is an appropriate marking on the packaging.
- 4.15.6.1 It is allowed to pack gaskets prepared in accordance with 4.15.2.1 in one box or keel.
5 Acceptance rules
- 5.1 A batch of gaskets at an enterprise is considered to be the number of gaskets of the same designation assigned by the product manufacturer, manufactured by this enterprise according to the same technical requirements in a certain period of time and intended for simultaneous delivery and acceptance.
- 5.2 To verify compliance of gaskets with the requirements of this standard, acceptance and periodic tests are carried out.
Acceptance tests are carried out according to 4.2.4.5.4.7—4.9.4.13.4.15.
Periodic tests are carried out according to 4.12 (Table 1. indicators 1 and 2). The frequency of monitoring is established in accordance with the requirements of the technical documentation of the enterprise.
Gaskets are checked for compliance with safety indicators according to 4.12 (Table 1. Indicators 3.4) for newly developed gaskets intended for serial production for the first time when putting products into production in case of disagreements between the consumer and the manufacturer, when the raw materials and materials used for the manufacture of gaskets change , affecting safety indicators.
- 5.3 To carry out acceptance and periodic tests of gaskets, 1% of product units (waste box), but not less than one product unit, are randomly selected from the batch, from which gaskets are selected in the quantity required for testing, but not less than 20 gaskets. If a batch of gaskets of the same class contains various technical and decorative designs, as well as quality characteristics, samples must be taken from all gaskets present in the unit of production.
- 5.4 If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeat tests are carried out on a double sample or sample. The results of repeated tests apply to the entire batch.
- 5.5 Research (tests) in order to assess compliance with legal requirements are carried out in an accredited testing laboratory (center).
Test reports carried out for the purposes of state registration may be included in the technical documentation confirming compliance with the requirements of this standard.
For testing, samples of each type of gasket are randomly selected in quantity. necessary for testing, but not less than three consumer packages for each type of test.
It is allowed to conduct research (tests) on experimental (laboratory) samples, which in design, composition and manufacturing technology must be identical to the products intended for sale to the buyer.
6 Test methods
- 6.1 Checking the technical and decorative performance of gaskets, their design and appearance is carried out visually by viewing gaskets selected according to 5.3.
- 6.2 Method for determining dye set-off
The method is based on the visual determination of traces of dye on filter paper soaked in a 0.9% sodium chloride solution after it comes into contact with a sample of the gasket and on the application of a load for a certain time.
- 6.2.1 Equipment and reagents:
- — a thermostat that provides the temperature for thermostatting (37 ± 2) °C. the height of the temperature control chamber is at least 18 cm, with a diameter of at least 19 cm;
- — flask according to GOST 1770 version 1. with a capacity of 1000 cm3;
- — vessel with a diameter of (200 ± 50) mm. with a capacity of at least 200 cm;
- — cargo weighing (1600 ± 36) g, cargo cross-sectional size — 30 to 30 mm with maximum deviations no more than ±3 mm;
- - tweezers;
- — organic glass plate with a thickness of (5 ± 1) mm. weighing (58 ± 2) g:
- - scissors;
- — thermometer in accordance with GOST 28498 with a division value of 1 °C;
- — measuring ruler in accordance with GOST 427 with a division value of 1 mm;
- • stopwatch;
- • distilled water according to GOST 6709;
- — filter paper according to GOST 12026;
- • sodium chloride according to GOST 4233.
- 6.2.2 Preparation of a 0.9% solution of sodium chloride (hereinafter referred to as the solution)
To prepare 1 dm3 of solution, take a sample of sodium chloride in an amount of (9.0 ± 0.1) g, transfer it to a flask and add distilled water to the 1 dm3 mark.
- 6.2.3 Preparation of test specimens
Three pads are selected at random from the sample selected by Lo 5.3. From each gasket, one sample measuring 30 x 30 mm is cut out with dimensional deviations of no more than ±2 mm. Cut out four sheets of filter paper measuring 60 x 60 mm with size deviations of no more than ±5 mm.
- 6.2.4 Test performance
8 vessel is filled with (100 ± 5) cm3 of solution. The temperature of the solution should be (37 ± 2) X. Four sheets of filter paper are immersed in the solution using tweezers until completely wetted, then removed. The test gasket sample with the painted side is placed on two sheets of moistened filter paper, covered on top with the remaining two sheets of moistened filter paper and transferred to the thermostat.
A plate of organic glass is placed on top of the filter paper, and a load weighing (1800 1 36) g is placed on it and left in a thermostat at a temperature of (3712) X for (2.0 ± 0.1) hours. After 2 hours, the weight, a plate of organic glass, and two sheets of filter paper are removed from the test sample and the presence of traces of paint on the filter paper, with which the test sample of the gasket was in contact with the painted side, is determined.
The gaskets are considered to have passed the test if, when testing each of the three samples, no traces of dye are found on the filter paper.
- 6.3 Width of the fixing layer, linear dimensions of spacers selected according to 6.4. determined using a measuring ruler LO GOST 427 with a division value of 1 mm.
- 6.4 Method for determining the complete moisture absorption of gaskets
The method is based on determining the mass of a 0.9% sodium chloride solution absorbed by the pad over a certain time.
- 6.4.1 Equipment and reagents:
vessel with a depth of at least 50 mm. with a capacity of at least 600 ml;
- — laboratory scales with an error of no more than ± 0.1 and a weighing limit of no more than 500 g:
- - stopwatch;
- — thermometer LO GOST 28498 with division price 1 X;
- — distilled water according to GOST 6709;
- - tweezers;
- — sodium chloride according to GOST 4233.
It is allowed to use measuring instruments, auxiliary equipment with similar metrological and technical characteristics, as well as reagents of a quality not lower than the above.
- 6.4.2 Preparation of 0.9% sodium chloride solution - according to 6.2.2.
- 6.4.3 Preparation of test specimens
Five pads are selected at random from the sample selected by Lo 5.3. The anti-adhesive layer is separated.
- 6.4.4 Test performance
The solution is poured into the vessel. The temperature of the solution should be (23 ± 2) X. Each pad is weighed to the nearest 0.01 g (weight of the sample in a dry state, from,).
Samples of gaskets are immersed in a vessel with a solution with the top coating layer down so that the samples are completely covered with the solution, and they are held until completely wet during the first 3-5 s. then, in a free state, the samples are kept in the solution for (30 ± 0.5) minutes.
Next, the gasket is removed from the vessel with the solution and suspended, clamping a slightly small part of the edge so that the solution drains. The sample is kept suspended for 5 minutes. and then weighed to the nearest 0.01 g (wet mass of the sample. t2).
- 6.4.5 Processing results
The complete moisture absorption of a single gasket K. g is calculated using the formula
K = t2-tg (1)
where m2 is the mass of the sample in a wet state (without anti-adhesive layer), g.
t, is the mass of the sample in a dry state (without anti-adhesive layer), g.
The arithmetic mean of the five determinations obtained is taken as the test result. The result is rounded to the first decimal place. The relative error in determining the total moisture absorption does not exceed ±10% with a confidence probability of P - 0.95.
- 6.5 Method for determining absorption time
The method is based on determining the time during which the gasket completely absorbs a certain amount of 0.9% sodium chloride solution applied to its surface from the side of the upper coating layer.
- 6.5.1 Equipment and reagents:
- — organic glass plate with a thickness of (5 ± 1) mm. size (100 ± 5) * (250 ± 5) mm. with hole diameter (20 ± 3) mm. with an inserted transparent tube with an internal diameter of 16 mm and a height of 65 mm (see Figure 1);
- — two weights weighing (500 ± 25) g each;
- — distilled water according to GOST 6709;
- — thermometer according to GOST 28498 with a division value of 1 'C,
- — a dispenser that supplies the required volume of solution;
- - marker:
- - stopwatch:
- — measuring ruler in accordance with GOST 427 with a division value of 1 mm;
- — sodium chloride according to GOST 4233.
It is allowed to use measuring instruments, auxiliary equipment with similar metrological and technical characteristics, as well as reagents of a quality not lower than the above.
- 6.5.2 Preparation of the solution - according to 6.2.2.
- 6.5.3 Preparation of test specimens
Five pads are selected at random from the sample selected in 5.3. The sample is placed on the stop so that the anti-adhesive layer of the product is on the bottom and with wings unfolded, if any.
- 6.5.4 Test performance
Determine and mark with a marker the center of the absorbent layer of the pad. 4 drops of the solution are added to the marked point using a pipette or dispenser, and then a 500 g weight is placed on top for 5 s to simulate body pressure. The weight is placed on a plate of organic glass with a thickness of (5 ± 1) mm. dimensions (100 ± 5) * (250 ± 5) mm without holes.
After 5 s, the weight is removed and the study continues.
A plate with a tube is placed on the sample so that the mark of the center of the absorbent layer of the gasket coincides with the center of the hole in the tube.
Weights are placed on the edges of the plate at equal distances from the edge to ensure uniform pressure on the gasket.
The dispenser is filled with 3 ml of solution. The solution temperature should be (23 ± 2) °C.
Figure 1 - Plexiglas plate with tube
Through a hole in the plate, a solution is supplied to the surface of the sample through a tube by a dispenser, and when the cylinder is filled with the entire volume of the solution, a stopwatch is started. This moment is taken as the beginning of the test. The moment of complete disappearance of the solution mirror visible in the hole of the plate is recorded.
- 6.5.5 Processing results
The arithmetic mean of the five determinations obtained is taken as the test result. The result is rounded to the first decimal place. The relative error of determination does not exceed ±10% with a confidence probability of P - 0.95.
- 6.6 The value of the change in pH of the aqueous extract is determined according to GOST 12523 with the following additions:
- - use distilled water with pH 5.4-6.6:
■ the extract from the gaskets is obtained at the ratio of the mass of the sample, g, to the volume of distilled water. cm3, like 1:100. use gaskets without destruction, keeping the samples for 6 hours at a temperature of 40 * C with periodic shaking (4-6 times);
- — the extract is filtered through a coarse glass filter into a small measuring cup, 2 ml of a 1 M potassium chloride solution is added according to GOST 4568 and measurement is started;
- — the deviation of the pH of the sample from the pH of the distilled water used should be no more than ±1.0.
- 6.7 Checking the markings and packaging of gaskets is carried out visually by comparing them with the requirements of this standard.
- 6.8 Hygienic indicators 4 of Table 1 are checked in accordance with regulatory and methodological documents: the amount of migrating harmful substances into distilled water is determined in accordance with GOST R 55227. [1]—(3); toxicity index - from [4] and (5): sensitizing effect - from GOST ISO 10993-10.
7 Transportation and storage
- 7.1 Transportation - according to GOST 6658-75 (section 3) by any type of covered transport in accordance with the rules for the transportation of goods applicable to this type of transport. Conditions of transportation - according to group 5 of GOST 15150.
- 7.2 Storage conditions for gaskets in transport packaging in consumer and manufacturer warehouses - according to group 5 of GOST 15150.
- 7.3 The shelf life of products is set by the manufacturer depending on the raw materials used for the manufacture of a specific gasket (group of gaskets).
Daily hygiene products
There are also several types of gaskets. The panty liner is intended for one-time use. They make it in a form similar to underwear. Every woman prefers to wear different panties: regular panties, shorts, thongs, tango. The panty liner should not stand out or go beyond the edges of the underwear. They are made without wings and come in different colors. The most common ones are white. This color is considered standard. It allows you to see the consistency and color of the discharge. React in a timely manner if diseases or abnormalities in the functioning of the genital organs appear. For the sake of aesthetic satisfaction of women's needs, panty liners are made black or a different color. There is plenty to choose from. The color range is presented in any product line of each manufacturer.
With daily use of disposable pads, women may experience an allergic reaction to the skin of the perineum and external genitalia. In order to prevent this situation, some manufacturers make the top layer of hygiene products natural. The division of types of pads according to the amount of absorbed secretions is not as diverse as the first type - for critical days. The packaging shows 1,2, maximum 3 drops. Based on this, panty liners vary in thickness.
Popular manufacturers
Rubber products according to GOST 7338-90
When purchasing, you should give preference to companies whose products undergo rigorous quality control.
The largest manufacturer is the PKF company. It offers customers pads:
- Rubber GOST 7338-90. They are made from food-grade, sponge, porous, vacuum, silicone rubber, with a diameter of 1 mm.
- Steel or Armco ring. There are products with oval or octagonal cross-section.
- Graphite unreinforced and reinforced with perforated stainless steel.
The products of the Recom pipeline parts plant are popular. There are such gaskets from this manufacturer:
- Metal ASME B16.20. They are suitable for extreme pressure and high temperature environments.
- Lens sealing rigid and compensating. Unlike others, they have one sealing area.
When choosing, it is important to consider whether the products have certificates of conformity of sealing gaskets in accordance with GOST and sanitary-epidemiological conclusions.
Reusable hygiene products
Among the types of gaskets, there are the following. Women use them for various reasons. Firstly, their composition is completely natural, which prevents the occurrence of gynecological diseases and skin irritations from synthetic compounds and other chemicals. Secondly, the cost of sanitary pads for critical days is not so small. Using reusable pads can save you a lot of money.
The production of such hygiene products falls on the shoulders of the woman. She chooses the shape, selects the fabrics. As a rule, the main layer for absorbing secretions of reusable pads is made of cotton wool. Several layers of gauze or natural fabric are placed on top. The gasket is stitched or left as is. To avoid leakage, the bottom layer is made of denser fabric or a piece of cellophane is sewn on.
Using reusable types of pads causes some difficulties. They do not retain moisture inside, change shape, and increase in size as secretions accumulate during menstrual periods. The main unpleasant moment is washing. Stains are removed with peroxide and laundry soap. The use of powders and bleaches is not recommended. Making reusable pads doesn't take much time. You can use them as long as the main layer of cotton wool is not damaged. Washing should be as gentle as possible; hygiene products should be dried while lying down. When hung, the appearance of reusable pads changes. Only clean ones can be used. For scanty discharge, simply fabric folded in several layers is used as pads. You should choose cotton fabric. A sheet or baby diaper will do.
Paronite, rubber gaskets for flange connections
The sealing and sealing of flange connections directly affects the amount of operating pressure that the pipeline can withstand during operation, as well as the reliability and safety of the system as a whole.
Flange gaskets
This article discusses gaskets for flange connections, their types, sizes and application features. We will study metal, paronite and rubber gasket materials and provide recommendations for their selection.
Functional purpose and need for use
Flange gaskets are a sealing material that, during operation, is in a compressed position between two flanges, which, due to the pressure of adjacent mounting plates, fills the free space between the connected ends of the pipeline.
When choosing a gasket material, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the working environment of the pipeline - its pressure, temperature, corrosive and chemical aggressiveness, as well as the configuration of the mating flange plates.
The following operational requirements are put forward for gasket products:
- elasticity;
- resistance to the work environment;
- corrosion resistance;
- absence of thermal deformations in a given temperature range;
- hardness, which should be less than that of the material from which the flanges are made, so that the gasket, when clamped, does not deform the surface of the fastening plate (taken into account when choosing metal products).
Flange joint sealing diagram
The gasket material installed between the two flanges fills the microscopic defects present on the front walls of the fastening plates - cavities, microcracks, depressions and roughness, which cause leaky connections.
During operation, the flange gasket experiences constant extrusion loads, which are created by internal pressure in the pipeline. To prevent leaks and depressurization of the joint, the pressure exerted by the bolts on the flange must create a mechanical stress sufficient to counteract the hydrostatic extrusion forces.
Medical pads
Manufacturers of hygiene products state that they must be used periodically, or even constantly, during menstruation. The use of medicinal types of pads makes it possible to avoid skin irritations, prevent diseases, and regulate the monthly cycle. You can choose based on the individual characteristics of the female body. There are 2 types of such hygiene products in pharmacies.
- Anion spacers
Medical pads are produced in the country of China. The cost is quite high. According to manufacturers, they prevent skin irritation and have anti-inflammatory, regenerating, and antibacterial effects. The top layer of the product is unique. Most likely, we are talking about ozone, which is used in the treatment of many gynecological diseases. Inside the layer there are additional substances of natural origin, in the form of herbal extract. Used for female diseases: fibroids, thrush, endometriosis.
- Pads with medicinal additives
The products are manufactured in China. The inner layer is impregnated with extracts and infusions of medicinal plants, which have long been used to treat gynecological diseases. They have an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. Soothe the skin during menstruation and restore hormonal levels. It is recommended to use it for almost all diseases of the female reproductive system.
The effectiveness of these funds is questionable; no studies have been conducted in our country.
How to choose a plumbing gasket
To determine the material you need, use the following table. The ++ sign indicates the preferred application for each material.
| Material/Application | HVS | DHW | Gas | Heating |
| Rubber | ++ | + | ||
| Paronitis | + | + | ++ | + |
| Photoroplast | + | + | + | ++ |
| Silicone | + | ++ | + | |
| Fiber | + | + | ++ |
Types of urological pads
Used by women with urinary incontinence. Constant leaks spoil underwear and permeate clothes with odor. The problem is solved with the help of urological pads. They are used by women after childbirth, when muscle tone decreases and the bladder cannot function normally. The use of urological pads is temporary. The situation with urinary incontinence occurs in women before menopause. The use of reusable pads or those used during menstruation is not suitable in this situation. The product is not able to eliminate the odor. The use of urological pads is not limited to this. The product is used for heavy periods. They differ from others in appearance and ability to absorb.
- Urological pads are characterized by their large size.
- There is a possibility of absorbing a large amount of liquid.
- The composition includes adsorbents that quickly eliminate odor.
- The top layer of urological pads is made of natural hypoallergenic fabric, which protects the skin from irritation.
Urological pads are changed as they are filled, but at least 2 times a day. Well-known manufacturers MoliMed, Seni, Tena. It is possible to choose the option that suits you more.
Product characteristics
Depending on the degree of incontinence, pads of different absorbency are distinguished; they can not only maintain dryness and protect underwear from contamination, but also neutralize unpleasant odors. A special adhesive base makes it possible to firmly fix the gasket and be sure of its reliability. The surface is impregnated with an antibacterial composition, which avoids irritation; this is very important especially during the postpartum period.
Urological pads for women are larger in size and absorbent than conventional sanitary pads, so their use completely eliminates any leakage and allows you to feel confident.
Test gasket
Used by pregnant women who are in their last months awaiting childbirth. The test makes it possible to determine the leakage of amniotic fluid. The appearance changes when liquid enters. The indicator turns blue. When exposed to urine, feces, or secretions, no reaction occurs. Blue spots appear in the presence of gynecological diseases during pregnancy. Allows you to take action in a timely manner.
Nowadays, a woman can choose pads for all occasions. The era of reusable pads is gradually becoming a thing of the past. Manufacturers are not going to stop there. It wouldn't be surprising if the next species appears soon. And the composition of the current ones will change.