When is conservative therapy prescribed, and when is surgery?
There are cases when it is preferable to choose conservative treatment of uterine fibroids without resorting to surgery:
- small myomatous nodes;
- clinical manifestations are mild;
- neighboring organs are functioning normally;
- there are contraindications to surgery.
Injections and tablets for uterine fibroids are used according to a specific scheme. In each case, it is individual and depends on the woman’s age, the nature and type of tumor, concomitant pathologies and diagnostic results. In what cases is it preferable to choose surgery:
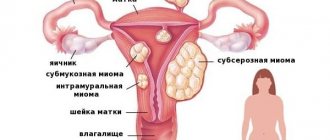
- The size of the neoplasm is from 12 weeks or more.
- There are associated pathologies (endometriosis, ovarian cysts).
- Dysfunction of neighboring organs due to tumor pressure on them.
- Severe pain and bleeding.
- Active tumor growth.
- Risk of degeneration into cancer.
In these cases, surgery is mandatory, but drug therapy is used as supportive therapy - to prepare for surgery, and after it to restore the body.
Types of Medicines
Drugs for fibroids can be either primary or additional treatment. If the tumor is small, less than 2 cm, then medications can completely cure it.
As drug therapy, experts prescribe:
- Hormonal medications.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Immunostimulants.
- Dietary supplements.
All medications must be prescribed by a doctor after diagnosis. For any changes in her condition, a woman should consult a doctor.
Action of the medicine
How does Lindinet 30 work? Reviews from gynecologists and instructions state that this drug is an oral monophasic contraceptive that can inhibit the secretion of pituitary (gonadotropic) hormones. The contraceptive properties of this medicine are associated with several mechanisms.
Ethinyl estradiol acts as the estrogenic component of this medication. This is a synthetic analogue of the hormone estradiol (follicular), which, together with the hormone of the corpus luteum, takes part in the regulation of the monthly cycle.
As for the gestagenic component, it includes gestodene, which is a derivative of 19-nortestosterone. In its selectivity and potency, it is superior not only to progesterone (or the so-called natural hormone of the corpus luteum), but also to other synthetic gestagens, including levonorgestrel.
Due to its high activity, the mentioned component is used only in reduced doses, in which it will not be able to exhibit androgenic properties and will not have any effect on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Antigonadotropins
These are products based on danazol and gestrinone. The following drugs are produced with these substances: Danogen, Danol, Danozol or Verodonazole and Nemestran.
They help with medium-sized fibroids up to three to four centimeters in diameter. Thanks to antigonatropins, such a neoplasm can resolve completely. If the fibroid is five centimeters or more, then it may decrease in size. There are side effects
- The voice becomes rough
- Body hair is actively growing
- Severe acne appears
The appointment is carried out strictly as prescribed by the gynecologist. The duration of treatment is determined individually.
Reviews from experts
Now you know why you need a product like Lindinet 30. The instructions and purpose of this medicine were presented above. What do gynecologists say about him? Most experts leave extremely positive reviews about this medication. They claim that such an oral contraceptive effectively helps resolve the issue of unwanted pregnancy.
Gynecologists also report that, in addition to their main purpose, the contraceptive pills in question are actively used as a therapeutic agent for gynecological pathologies, including functional disorders of the monthly cycle.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
Thanks to a carefully developed formula, as well as a thoughtful regimen for taking the contraceptive, you can easily achieve the desired results for a long time. At the same time, gynecologists claim that Lindinet 30 tablets can cause adverse reactions. In this regard, before taking them, you should definitely seek additional advice from an experienced specialist.
Gestagens
For macular fibroids, drugs based on gestagens can be prescribed. They are quite effective and safe. The pills stop the synthesis of estrogen in the body. But unlike antagonistic drugs, they act more gently.
Therefore, they are more often used as maintenance therapy. The most popular gestagens:
- Duphaston;
- Norkolut;
- Orgametril;
The drugs are prescribed only by a gynecologist. And they are taken under strict control, since in some cases the opposite effect occurs - the nodes begin to actively grow.
Antiprogestogens
These drugs are quickly absorbed and affect progesterone. Reducing the effect of progesterone contributes to the regression of fibroids with sizes less than 4 cm. A well-known drug is Mifepristone.
Available in tablet form. It not only promotes the resorption of the node, but also reduces symptoms. Therefore, it is also used before surgery to remove fibroids. The course of treatment and dosage regimen are determined by the doctor individually, depending on the type of tumor and its size. Contraindications: thrombosis, endocrine diseases, cardiovascular and renal failure. Side effects - hot flashes. But they rarely occur.
Combined oral contraceptives
Combined hormonal drugs are often prescribed for fibroids. They reduce the manifestation of symptoms, can reduce the size of the node, and normalize the cycle, and prevent the development of complications. This type of contraceptive is called monophasic. That is, all active components are distributed in equal proportions, regardless of the day of the cycle.
Hormones found in COCs:
- Estrogen – normalizes the formation of the mucous layer of the uterus (endometrium)
- Progestogen – prevents pregnancy.
Now, an analogue of estrogen in tablets is ethinyl estradiol. And Progestogen Levonorgestrel, Gestogen. What combined oral contraceptives are prescribed for uterine fibroids:
- Rigevidon;
- Jess;
- Janine;
- Yarina;
- Lindinet 30.
All these drugs can be taken only as prescribed and under the supervision of a gynecologist.
Related article: contraceptives for uterine fibroids
Janine with uterine fibroids
This drug is a type of antiandrogen. Available in the form of round dragees in a smooth, white shell. The drug contains ethinyl estradiol and dienogest, as well as auxiliary components. (potato starch, sucrose, magnesium stearate, macrogol).
Acts as a contraceptive, preventing conception. In addition, Janine acts as a medicine for menstrual pain, stabilizes the periodicity of the cycle, normalizes the condition of the facial skin, and protects against anemia caused by heavy bleeding.
Contraindications for use:
- allergic reaction to substances in the drug;
- thrombosis;
- ischemic crises, instability of cerebral circulation;
- migraine attacks;
- diabetes;
- abdominal surgery;
- arterial type hypertension;
- pancreatitis;
- liver failure;
- malignant neoplasms;
- uterine bleeding of unknown pathogenesis;
- pregnancy and lactation.
Janine is also not recommended for women who smoke. There may be side effects when taking the drug. Possible:
- Nausea and vomiting, diarrhea.
- Hunger.
- Increase or decrease in pressure.
- Changes in vaginal microflora, fungal pathologies.
- Infectious diseases of the genital tract and organs.
- Depressive state, nervousness.
- Dandruff, hair loss.
- Pain in the muscles of the legs and arms.
- Allergy.
If the recommended dose is exceeded, vomiting and nausea may occur. Spotting brown discharge from the vagina appears. If side effects occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. Instructions for use for uterine fibroids:
- The course of treatment is 12 weeks without a break.
- After 12 weeks – break for 7 days
During the week's break, your period comes. The woman undergoes an examination and, if necessary, another three-month course of Janine is prescribed. Among the analogues of the drug, Siluet is known.
Reviews
Inna, 30 years old
I had a small fibroid. They didn’t want to operate, so they assigned Janine. In the first days I felt weak and wanted to vomit, but then everything went away. I took the drug for six months. During this time, the tumor decreased in size and then completely resolved. There were no relapses, and a year later I became pregnant.
Medication "Lindinet 30": instructions for use
The medicine in question is prescribed one tablet per day for 21 days, at the same time. After taking the last dosage, take a week break. Then the use of the medicine is resumed. The first tablet of this medication should be taken from the first to the fifth day of the monthly cycle.
If the patient switches to Lindinet 30 from another oral contraceptive, then the first tablet must be taken immediately after taking the last dosage of another hormonal drug.
After an abortion at the very beginning of pregnancy, the use of the medication can be started immediately after the operation. There is no need to use other methods of contraception.
After childbirth or abortion in the second trimester, you can start taking the medicine on the 22-28th day. In this case, it is necessary to use other means of contraception in the first week.
If you miss a dose, take the pill as soon as possible. If the interval between doses of the medication is less than 12 hours, the contraceptive effect is not reduced. In this case, it is not necessary to use other methods of contraception.
If the interval is more than 12 hours, the contraceptive effect of the medicine may decrease. In this situation, additional methods of contraception must be used in the next week.
If diarrhea and vomiting begin within 4 hours after using the medicine, its contraceptive effect may be reduced. In such cases, you must follow the instructions for skipping pills.
To speed up the onset of menstruation, you should shorten the break in taking the medication. To delay the onset of menstruation, the medication should be continued without a weekly break.
Klaira for uterine fibroids
The drug Klayra is distinguished by the fact that it consists of hormones of natural origin. Recommended for young women of childbearing age. It is based on estradiol valerate and dienogest. Qlaira is prescribed by a doctor for uterine fibroids and endometriosis. One package contains 28 multi-colored dragees, which contain different ingredients. Qlaira has an effect on a woman’s hormonal background, reducing the level of female hormone in the blood. The growth of fibroids stops; if you take the drug in full, the tumor may decrease in size. You can take pills for fibroids according to the usual contraceptive regimen, starting from the 1st day of the menstrual cycle and without breaks.
Contraindications for use:
- vascular diseases;
- heart failure;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- high blood pressure;
- menopause;
- renal and liver failure;
- pancreatic diseases;
- migraine in any form;
- depressive disorders;
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Side effects include excess weight, acne, headaches, swelling of the mammary glands, and bleeding. As analogues of the drug, Novinet, Yarina, Regulon can be used.
Reviews
Natalya, 25 years old
I haven’t given birth yet, so the doctor prescribed me the drug Qlaira. After two months, the fibroids stopped growing. And after five it became smaller. I didn’t take breaks like with regular contraception, but everything was normal, the only thing was nausea and diarrhea in the first week. The doctor said that I could get pregnant in about a year and a half after finishing treatment.
Nuvaring
Nuvaring is a vaginal ring with estrogen and progesterone, which doctors place both to shrink small fibroids and after surgery to remove the tumor. The product acts as a local contraceptive. And it does not affect the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys. It acts as a prophylactic against the recurrence of fibroids and the appearance of endometriosis. The ring normalizes the cycle, reduces menstrual pain and does not lead to weight gain.
How to use:
The ring is inserted into the vagina once a month. A woman needs to choose a comfortable position. Squeeze the ring and gently insert it into the vaginal area until it reaches a comfortable position. You need to introduce a new one exactly in a month, at the same time. Side effects:
- depression and nervousness;
- decreased libido;
- spotting;
- pain in the stomach.
If you experience severe pain and spotting bleeding that does not go away, you should consult a doctor.
Femoston
Another combined hormonal drug is Femoston. Femoston has an anti-menopausal effect; it is prescribed after surgery to remove uterine fibroids as hormone replacement therapy.
The drug contains estrogen and dydrogesterone. The drug normalizes hormonal levels, prevents high blood pressure, osteoporosis and atherosclerosis. Contraindications for use: renal failure, vascular diseases, oncology. The duration of treatment is determined individually.
Silhouette
Silhouette for uterine fibroids is used as an analogue of “Janine” tablets. This is a monophasic hormonal drug. It relieves inflammation, prevents the formation of endometriosis, and prevents further growth of fibroids.
How to use Siluet in the treatment of fibroids: tablets are taken daily for three months, with breaks of one week.
Utrozhestan
Unlike other COCs, Ugrozhestan can be taken during pregnancy with fibroids. It belongs to a type of gestagenic drugs based on progesterone.
The product prevents endometriosis and reduces the amount of female hormone. For fibroids, the drug can be prescribed vaginally to reduce the effect on the digestive and excretory systems of the body. Contraindicated in: porphyria, epilepsy, venous diseases.
Lindynette 30
If any of the conditions, diseases or risk factors listed below currently exist, the potential risks and expected benefits of using COCs, including the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol, should be carefully weighed in each individual case and discussed with the woman before starting to take the drug. If any of these conditions, diseases or risk factors worsen, intensify or appear for the first time, a woman should consult her doctor to decide whether to stop taking the drug.
Risk of developing venous and arterial thromboembolism (VTE and ATE)
The results of epidemiological studies indicate a relationship between the use of COCs and an increased incidence of venous and arterial thrombosis and thromboembolism (such as DVT, PE, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disorders). These diseases are rare.
The increased risk of developing VTE associated with the use of COCs is due to the presence of estrogen in its composition. COCs containing levonorgestrel, norgestimate or norethisterone as a progestogen component are associated with the lowest risk of VTE. When using other COCs, such as the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol, the risk of developing VTE is twice as high.
The choice of a COC with a higher risk of VTE should only be made after consultation with the woman to ensure that she fully understands the risk of VTE associated with the contraceptive, the effect of the drug on her existing risk factors and that the risk of developing VTE maximum in the first year of taking such drugs. An increased risk is also observed when COC use is resumed (after a break between doses of the drug of 4 weeks or more). The increased risk of developing VTE is present primarily during the first 3 months.
VTE can be life-threatening or lead to death (in 1-2% of cases). VTE, manifested as DVT and/or PE, can occur with all COCs.
It is extremely rare when using COCs that thrombosis of other blood vessels occurs, for example, hepatic, mesenteric, renal, cerebral veins and arteries or retinal vessels.
Symptoms of DVT:
unilateral swelling of the lower limb or along the vein, pain or discomfort only in an upright position or when walking, local increase in temperature, redness or discoloration of the skin in the affected lower limb.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism:
difficulty or rapid breathing; sudden cough, including with hemoptysis; sharp pain in the chest, which may intensify with deep inspiration; sense of anxiety; severe dizziness; fast or irregular heartbeat. Some of these symptoms (eg, shortness of breath, cough) are nonspecific and may be misinterpreted as signs of other more common and less severe conditions (eg, respiratory tract infection).
ATE can lead to stroke, vascular occlusion, or myocardial infarction.
Symptoms of a stroke
: sudden weakness or loss of sensation in the face, limbs, especially on one side of the body, sudden confusion, severe or prolonged headache for no apparent reason, one- or two-sided loss of vision; problems with speech and understanding; sudden disturbance in gait, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination; sudden loss of consciousness or fainting with or without a seizure.
Other signs of vascular occlusion
: sudden pain, swelling and slight cyanosis of the extremities, “acute” abdomen.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
: pain, discomfort, pressure, heaviness, a feeling of compression or fullness in the chest or behind the sternum, radiating to the back, jaw, upper limb, epigastric region; cold sweat, nausea, vomiting or dizziness, severe weakness, anxiety or shortness of breath; fast or irregular heartbeat. ATE can be life-threatening and lead to death.
In women with a combination of several risk factors or high severity of one of the factors, the possibility of their mutual reinforcement should be considered. In such cases, the degree of increase in risk may be higher than with a simple summation of factors. In this case, taking the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol is contraindicated.
The risk of developing thrombosis (venous and/or arterial) and thromboembolism or cerebrovascular disorders increases:
-with age;
- in women who smoke (with an increase in the number of cigarettes or an increase in age, the risk increases, especially over the age of 35);
- if there is a family history (for example, VTE or ATE in close relatives or parents aged less than 50 years). In the case of a hereditary or acquired predisposition, the woman should be examined by an appropriate specialist to decide on the possibility of taking COCs;
- for obesity (with a BMI more than 30 kg/m2);
- with dyslipoproteinemia;
- for arterial hypertension;
- for migraine;
- for diseases of the heart valves;
- with atrial fibrillation;
- in case of prolonged immobilization, serious surgery, any operation on the lower extremities, in the pelvic area or extensive trauma.
In these cases, the use of COCs should be stopped (in the case of planned surgery, at least four weeks before it) and not resumed for two weeks after the woman has fully regained mobility.
Temporary immobilization (eg, air travel lasting more than 4 hours) may also be a risk factor for the development of VTE, especially in the presence of other risk factors.
The possible role of varicose veins and superficial thrombophlebitis in the development of VTE remains controversial.
The increased risk of thromboembolism in the postpartum period should be taken into account. Peripheral circulatory disorders may also occur in diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, hemolytic uremic syndrome, chronic inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis) and sickle cell anemia.
An increase in the frequency and severity of migraine (which may precede cerebrovascular events) during the use of COCs is grounds for immediate discontinuation of these drugs.
Biochemical indicators indicating a hereditary or acquired predisposition to the development of venous or arterial thrombosis include: resistance to activated protein C, hyperhomocysteinemia, antithrombin III deficiency, protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency, antiphospholipid antibodies (anticardiolipin antibodies, lupus anticoagulant).
When assessing the risk-benefit ratio, it should be taken into account that adequate treatment of the relevant condition/disease may reduce the associated risk of thrombosis.
Tumors
The most significant risk factor for the development of cervical cancer (CC) is persistent human papillomavirus infection. There are reports of a slight increase in the risk of developing CC with long-term use of COCs. However, the connection with taking COCs has not been proven. Controversy remains regarding the extent to which these findings are related to screening for cervical pathology or to sexual behavior patterns (less use of barrier methods of contraception, greater number of sexual partners).
A meta-analysis of 54 epidemiological studies showed that there is a slightly increased relative risk of developing breast cancer diagnosed in women currently taking COCs (relative risk 1.24). The increased risk gradually disappears within 10 years of stopping these drugs. Due to the fact that breast cancer is rare in women under 40 years of age, the increase in the incidence of breast cancer in women who are currently taking COCs or have recently taken it is insignificant in relation to the overall risk of this disease. Its connection with COC use has not been proven. The observed increase in risk may also be a consequence of earlier diagnosis of breast cancer in women using COCs (they are diagnosed with earlier clinical forms of breast cancer than women not taking COCs), the biological effects of COCs, or a combination of both of these factors.
In rare cases, during the use of COCs, the development of benign, and in extremely rare cases, malignant liver tumors, which in some cases led to life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding, was observed. In case of severe abdominal pain, liver enlargement or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding, this should be taken into account when making a differential diagnosis.
Other states
Depressed mood and depression are known adverse reactions when using hormonal contraceptives. Depression can be a serious disorder and is a known risk factor for suicidal behavior and suicide. Women should be advised to contact their doctor if mood changes or depressive symptoms occur, including soon after starting treatment.
In women with hypertriglyceridemia (or a family history of this condition), the risk of developing pancreatitis may increase while taking COCs.
Although slight increases in blood pressure have been described in many women taking COCs, clinically significant increases have rarely been reported. However, if a persistent clinically significant increase in blood pressure develops during the use of COCs, the COC should be discontinued and treatment of arterial hypertension should be initiated. COC use can be continued if normal blood pressure values are achieved with antihypertensive therapy.
The following conditions have been reported to develop or worsen both during pregnancy and while taking COCs, but their relationship with COC use has not been proven: cholestatic jaundice and/or pruritus associated with cholestasis; formation of gallstones; porphyria; systemic lupus erythematosus; hemolytic-uremic syndrome; chorea; herpes during pregnancy; hearing loss associated with otosclerosis. Cases of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis have also been described with the use of COCs.
In women with hereditary forms of angioedema, exogenous estrogens may cause or worsen symptoms of angioedema.
Acute or chronic liver dysfunction may require discontinuation of COCs until liver function tests return to normal. Recurrence of cholestatic jaundice, which developed for the first time during a previous pregnancy or previous use of sex hormones, requires discontinuation of COC use.
Although COCs may have an effect on insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, in patients with diabetes mellitus using low-dose COCs, as a rule, no dose adjustment of hypoglycemic drugs is required. However, women with diabetes mellitus should be carefully monitored while taking COCs.
Chloasma can sometimes develop, especially in women with a history of pregnancy chloasma. Women with a tendency to chloasma should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and exposure to ultraviolet radiation while taking COCs.
Effect on liver function tests
In clinical studies involving patients receiving hepatitis C viral therapy (a combination of drugs containing ombitasvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, dasabuvir, with or without ribavirin), increases in ALT activity more than 5 times the upper limit of normal were recorded more often in patients using ethynyl-containing COCs.
If a course of therapy with this combination of drugs is necessary, a patient using the contraceptive drug gestodene + ethinyl estradiol should be switched to alternative methods of contraception (non-hormonal or contraceptives containing only gestagen) before starting the course of treatment. You can resume taking the combination of gestodene + ethinyl estradiol no earlier than 2 weeks after the end of the course of therapy with antiviral drugs.
Laboratory tests
The use of drugs such as gestodene + ethinyl estradiol may affect the results of some laboratory tests, including biochemical indicators of liver, thyroid, kidney and adrenal function, the concentration of transport proteins in plasma (for example, transcortin, lipid / lipoprotein fractions, parameters of carbohydrate metabolism, coagulation and fibrinolysis). These changes usually remain within normal physiological values.
Reduced efficiency
The effectiveness of COCs may be reduced in the following cases: in case of missed pills, gastrointestinal disorders or as a result of drug interactions.
Effect on bleeding pattern
While taking COCs, irregular bleeding may occur (“spotting” and/or “breakthrough” bleeding), especially during the first months of use. Therefore, any irregular bleeding should be assessed only after an adaptation period of approximately 3 cycles of dosing.
If irregular bleeding recurs or develops after previous regular cycles, careful evaluation should be performed to rule out malignancy or pregnancy.
Some women may not develop bleeding during a break in taking pills. “ooContraindications” and “With caution.”
-Local compaction in the mammary gland.
-Concomitant use of other medications.
-If prolonged immobilization is expected (for example, a cast is applied to the lower extremity), hospitalization or surgery is planned (at least four weeks before the proposed operation).
-Unusually heavy bleeding from the vagina.
-Missed a pill in the first week of taking the drug and had sexual intercourse seven days or less before.
- Absence of regular menstrual-like bleeding two times in a row or suspicion of pregnancy (you should not start taking pills from the next package before consulting your doctor).
You should stop taking the tablets and consult your doctor immediately if there are possible signs of thrombosis, myocardial infarction or stroke: unusual cough; unusually severe pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left arm; unexpected shortness of breath, unusual, severe and prolonged headache or migraine attack; partial or complete loss of vision or double vision; slurred speech; sudden changes in hearing, smell, or taste; dizziness or fainting; weakness or loss of sensation in any part of the body; severe abdominal pain; severe pain in the lower limb or sudden swelling of any of the lower limbs.
This medicine contains lactose (in the form of lactose monohydrate) and sucrose. Patients with rare hereditary diseases such as galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, as well as rare congenital forms of fructose intolerance or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency should not take this drug.
Norkolut
Norkolut for fibroids is effective for small and medium-sized tumors that do not grow quickly. It belongs to the type of gestagenic drugs. It contains noritesterone. The drug normalizes hormonal levels, reduces the rate of tumor growth, reduces the risk of developing endometriosis and stabilizes the hormonal cycle.
Indicated for subserous fibroids, accompanied by thickening of the endometrium, adenomyosis and uterine bleeding. The dosage regimen for fibroids is prescribed by a doctor. Usually it is as follows: one or two tablets per day, starting from the fifth day of the cycle until the twenty-fifth day. Duration of therapy is from 12 to 24 weeks.
Adverse reactions
What side effects can the drug Lindinet 30 cause? Reviews from gynecologists (for fibroids, this medicine can only be taken on the doctor’s recommendations) claim that the medication in question should be stopped immediately if it causes the following reactions:
- arterial hypertension, hearing loss caused by otosclerosis, venous and arterial thromboembolism;
- hemolytic-uremic syndrome, venous or arterial thromboembolism of mesenteric, hepatic, retinal and renal veins and arteries;
- porphyria, Sydenham chorea, exacerbation of reactive lupus erythematosus.
Other side effects of this drug that do not require discontinuation are the following:
- migraine, candidiasis, acyclic bleeding from the vagina, galactorrhea, amenorrhea after drug withdrawal, pain, changes in vaginal mucus, enlarged mammary glands, development of inflammation in the vagina, tension;
- ulcerative colitis, headache, liver adenoma, epigastric pain, cholelithiasis, nausea, hepatitis, vomiting, exacerbation of jaundice, Crohn's disease;
- exudative erythema, depression, erythema nodosum, chloasma, rash, hair loss;
- increased sensitivity of the cornea, decreased hearing;
- mood lability, decreased tolerance to carbohydrates, water retention in the body, hyperglycemia, changes in body weight, increased TG levels;
- allergy.
Mifepristone
If the growth of fibroids is provoked by an increased level of progesterone, then Mifepristone is prescribed. It helps normalize progesterone, preventing tumor growth. In addition, it increases the tone of the uterine muscles. Recommended for the treatment of small and medium-sized fibroids for a period of twelve weeks.
Contraindications, in addition to the usual ones for oral contraception, are more than two months of pregnancy, large uterine fibroids, cysts on the ovaries, hemostatic pathologies. Incompatible with glucocosteroids. Not recommended for women over 35 years of age. Possible side effects:
- hyperthermia;
- exacerbation of genitourinary system infections;
- reduction of the reproductive organ;
- weakness in the body.
If you take the drug for more than 12 weeks in a row, you will experience a lack of menstruation.
Herbal preparations
Plant-based preparations for the treatment of uterine fibroids play a supporting role and reduce the symptoms of the disease. They are also used to reduce tumor growth.
Biomycin
The product is based on phytohormones - indole-3, carbinol, Eligallate. It is effective for all types of tumors caused by hormonal imbalance. Myomin has antitumor properties, relieves pain, reduces bleeding, activates the immune system, and prevents the development of endometriosis.
It can also be used as a prophylactic agent after removal of fibroids. Instructions for use: twice a day with meals, one tablet. The duration of the course is determined by the doctor. There are practically no contraindications for use, except for individual intolerance.
Cyclodinone
This remedy stabilizes estrogen levels in fibroids. The active ingredient is Vitex extract, as well as vitamins and other beneficial substances. Helps reduce symptoms of the disease.
Mastodinon
Mastodion is also used as an adjuvant in the treatment of fibroids. It regulates progesterone, helps restore the cycle, and has a resolving effect on the tumor if it is caused by a lack of progesterone.
Release form: tablets or drops. How to use:
- Dragee – 1 tablet twice a day.
- Drops – 30 drops per 250 ml of clean water.
Duration of therapy is 12 weeks or more. Contraindications: thrombophlebitis, pancreatic diseases, heart failure.
Befungin
Product based on herbal ingredients with tree fungus extract. Activates the body's defense system, normalizes metabolic processes, restores damaged tissue, reduces pain and bleeding, and normalizes the functioning of endocrine systems. Available in liquid form. The drug is recommended for the symptomatic treatment of fibroids or restoration of the body after its removal.
How to take: two teaspoons of solution for half a glass of boiled water. Drink one teaspoon three times a day half an hour before meals. The duration of treatment is determined individually, on the recommendation of a doctor.
Remens
Remens is one of the drugs for the treatment of uterine fibroids, used for the symptomatic treatment and prevention of endometriosis, and normalization of the emotional background. Suitable for both women of childbearing age and those entering menopause.
The drug contains only herbal ingredients. Contains:
- Black cohosh extract
- Sanguinaria canadensis extract
- Pilocarpus extract
- Extract from cuttlefish glands
- Snake venom extract
Directions for use: one tablet three times a day, half an hour before meals. The duration of treatment is three months, then a break for four weeks.
The product has no contraindications or side effects, except for individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Additional drugs
Drug treatment of fibroids also includes other drugs to support the body and reduce symptoms of the disease, in addition to hormonal ones.
Most often these are Wobenzym and Tranexam.
- Wobenzym is a drug consisting of plant extracts and extracts of animal origin. It reduces the negative effects of hormones, prevents inflammatory processes, and protects against chronic infections. The course of treatment is 8 weeks. The drug is taken only in combination with combined oral contraceptives. It has virtually no side effects.
- Tranexam is recommended for severe bleeding. Contains pancreatin, papain, rutoside, bromelain, trypsin and lipase. Contraindications include individual intolerance to the drug and blood diseases. The dosage regimen is determined individually, depending on the severity of the disease. Side effects include individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Dietary supplements for fibroids
Dietary supplements cannot act as drugs for fibroids. But they contribute to the resorption of the tumor when it is small.
The advantage of dietary supplements is the absence of side effects. They restore the balance of vitamins and minerals, help cope with depression and nervousness, and normalize metabolism.
Estrovel
This remedy stabilizes hormone levels. Made on a natural basis. Available in capsule form. Contains a complex of vitamins B and amino acids. Capsules strengthen the body's defense system and give a surge of strength.
Relieves stress, helps stabilize the cycle and prevents anemia. How to take: 1-2 capsules per day, during meals. The course of treatment is eight weeks. It can be combined with other drugs and has no contraindications or side effects.
Indinol and Indol forte
Indinol tablets are made with broccoli extract. Reduces the level of estrogen in the blood, which helps stop the growth of the tumor. Indinol should be taken two capsules per day. The course of treatment is six months. Indole Forte – one capsule once a day with meals.
Mirena spiral
The Mirena spiral is often prescribed for uterine fibroids, as it relieves the symptoms of the disease and helps reduce the tumor, like similar oral medications. But at the same time, it does not have a negative effect on the kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system.
The spiral works locally, releasing a dose of hormones into the uterine area every day. In addition, the IUD has a contraceptive effect, preventing conception, without side effects. The installation period for the spiral is five years.
Kinetic ability
How does the absorption of a medication such as Lindinet 30 occur? The instructions indicate that after taking the medicine, its main substances are quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
With a single dose of the drug, its peak concentration in the blood is reached after 1 hour. The bioavailability of this medicine is 98.9%.
Gestodene binds to globulin and albumin. It undergoes biotransformation in the liver and is excreted from the body only in the form of derivatives along with feces and urine.
As for ethinyl estradiol, it undergoes aromatic hydroxylation. In this case, hydroxylated and methylated metabolites are formed. Ethinyl estradiol is excreted only in the form of derivatives, along with bile and urine in a ratio of 3:2.